What is DNA?
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid, is the polymer of nucleotides. Every living thing has DNA, for example plants, animals, bacteria etc. Most importantly human's genetic material is also DNA, which makes us unique! DNA contains the hereditary information which passes on to you from your parents. DNA is mainly located in cell nucleus and small amount of DNA is also present in mitochondria which is known as mitochondrial DNA.
- DNA is long strand of 2 polynucleotides which wind one another to form a double helix structure.
- Each composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar (known as nucleoside) and phosphate group are known as nucleotide (also known as nucleoside phosphate). Nitrogenous bases are of 4 types such as Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T).
- The bases of one strand bind with the other strand to form purine (2 ring structure) to pyrimidine (1 ring structure) that is A.T and G.C bases pairs through hydrogen bonds.
- Due to the bond angle of the sugar phosphate molecule, the linkages form a double helix structure.
- Each strand of DNA has one 5'-P and 3'-OH at each end of the helix. One strand run in 5'-3' (sense strand) direction whereas other one in 3'-5' (antisense strand) which make them antiparallel.
DNA and its building blocks
Several types of bonds present in DNA double helix
- A nucleotide or nucleoside phosphate is formed by the attachment of phosphate group to the 5' position of nucleoside by ester linkage.
- Nucleotides are joined together by attaching 5' phosphate of one nucleotide to 3' hydroxyl of another nucleotide by phosphodiester linkage between the adjacent sugars.
- A purine base in one strand is bonded to pyrimidine base in the another strand via hydrogen bond. Adenine pairs with Thymine by 2 hydrogen bonds and Guanine pairs with Cytosine by 3 hydrogen bonds.
Denaturation and Melting temperature
- The loss of helical structure of DNA is known as denaturation. This occurs by the disruption of hydrogen bonds at elevated temperatures.
- The temperature at which half of the DNA molecules are denatured, which is known as melting temperature of DNA.
Measurement of DNA Denaturation
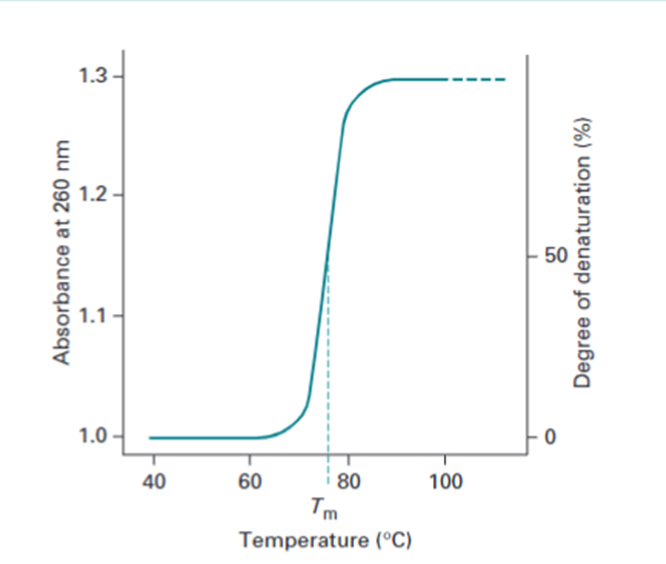
Melting curve of DNA
DNA denaturation is measured by using spectrophotometer. The aromatic rings in the nucleotide bases absorbs light in UV range, so the DNA also. The bases absorb 260nm light strongly.
- The double stranded DNA has less absorbance of light at 260nm compared to single stranded DNA, because of the interference by the double helix structure of the DNA.
- As the temperature increases DNA denatures and becomes single stranded, So absorbance increases.
References
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2002. The Structure and Function of DNA. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26821/
What is DNA? (2022, February 18). Yourgenome. https://www.yourgenome.org/facts/what-is-dna
- Freifelder, D. (1990). Molecular biology (2nd ed.). Narosa Publishing House.
- W. (2010). Principles and Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (7th ed.). Cambridge India
Let me know the suggestions if any! Keep reading!





No comments:
Post a Comment